交换机
四种类型的交换机:
- Fanout Exchange —— 扇形
- Direct Exchange —— 直连
- Topic Exchange —— 主题
- Headers Exchange —— 头部
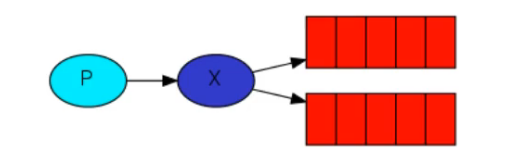
扇形交换机
投递到所有的与之相绑定队列中,不需要路由键,也自然不需要路由键匹配。相当于广播或者群发
Java案例(配置)
java
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration // Rabbit配置类
public class RabbitConfig {
@Bean // 定义交换机
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
// 为交换机取名字
return new FanoutExchange("exchange.fanout");
}
@Bean // 定义队列 A
public Queue queueA() {
return new Queue("queue.fanout.a");
}
@Bean // 定义队列 B
public Queue queueB() {
return new Queue("queue.fanout.b");
}
/*
* Spring容器就是一个Map集合使用 @Bean 定义的对象都会被存到这个集合中
* 集合的 KEY 就是方法名称
* 集合的 Value 就是方法的返回值
*
* 所以在下面交换机绑定队列所传递的形参名字就是容器中的KEY
* */
// 绑定队列A和交换机
@Bean
public Binding bindingA(FanoutExchange fanoutExchange, Queue queueA) {
// 因为是扇形交换机所以不需要绑定KEY
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueA).to(fanoutExchange);
}
// 绑定队列B和交换机
@Bean
public Binding bindingB(FanoutExchange fanoutExchange, Queue queueB) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueB).to(fanoutExchange);
}
}Java案例(测试)
java
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class MessageTest {
@Resource // 也可以使用 AmqpTemplate 因为 Amqp 是一个协议 Rabbit 实现了 Amqp
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@GetMapping("/message") // 发送消息
public void sendMessage(String msg) {
Message message = new Message(msg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange.fanout", "", message);
log.info("发送消息成功:{}", msg);
}
// 监听A队列 - 如果之前队列中有未消费数据会在重启之后全部消费
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue.fanout.a")
public void receiveMessageA(Message msg) {
log.info("A接收到消息:{}", new String(msg.getBody()));
}
// 监听B队列 - 如果之前队列中有未消费数据会在重启之后全部消费
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue.fanout.b")
public void receiveMessageB(String msg) {
log.info("B接收到消息:{}", msg);
}
}使用 @RabbitListener 注解监听队列。使用 queues 指定监听队列名字,也可以同时监听两个队列,使用以下写法
java
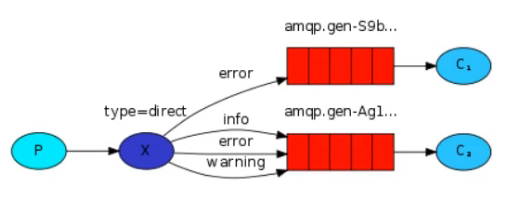
@RabbitListener(queues = {"queue.fanout.a","queue.fanout.b"})直连交换机
根据路由键精准匹配进行路由消息队列
在发送消息过程中,如果路由Key与队列中任意一个都不匹配,那个该消息会直接被交换机丢弃
Java案例(配置)
java
@Bean // 定义交换机 - 建造者模式
public DirectExchange directExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("exchange.direct").build();
}
@Bean // 定义队列 A
public Queue queueA() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("queue.fanout.a").build();
}
@Bean // 定义队列 B
public Queue queueB() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("queue.fanout.b").build();
}
// 绑定队列A和交换机并绑定键(error)
@Bean
public Binding bindingA(DirectExchange directExchange, Queue queueA) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueA).to(directExchange).with("error");
}
// 绑定队列B和交换机并绑定键(info)
@Bean
public Binding bindingB1(DirectExchange directExchange, Queue queueB) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueB).to(directExchange).with("info");
}
// 绑定队列B和交换机并绑定键(error)
@Bean
public Binding bindingB2(DirectExchange directExchange, Queue queueB) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueB).to(directExchange).with("error");
}在构造队列的时候使用
durable是保证队列持久化的一个方法;持久化也就是在RabbitMQ重启时队列内容不丢失,就是说把内存中的东西保存到磁盘上保证不丢失。与之相对应的还有一个非持久化的方法nonDurable
Java案例(测试)
java
@GetMapping("/message") // 发送消息
public void sendMessage(String msg) {
Message message = MessageBuilder.withBody(msg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)).build();
// 交换机的名字 - 键 - 消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange.direct", "info", message);
log.info("发送消息成功:{}", msg);
}
// 监听A队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue.direct.a")
public void receiveMessageA(Message msg) {
log.info("A接收到消息:{}", new String(msg.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
// 监听B队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue.direct.b")
public void receiveMessageB(String msg) {
log.info("B接收到消息:{}", msg);
}在以上案例中交换机 exchange.direct 分别绑定了队列A和队列B,在这两个队列中分别指定不同的路由键。在发送消息时以配置为准键设置为 error 时发送消息,那么AB队列都会接收到消息并输出;如果键为 info 时那么B队列会执行
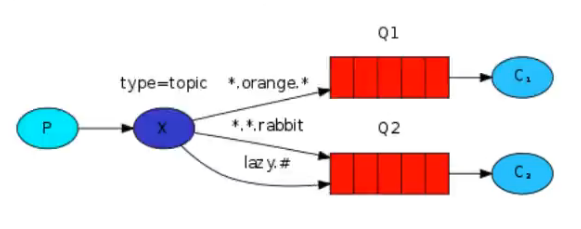
主题交换机
相当于SQL模糊匹配
# 匹配多个单词:用来表示任意数量(一个或者多个)的单词
* 匹配一个单词:用来匹配一个也只能是一个单词
单词:使用 . 隔开的为单词如
queue.# == queue.a,queue.a.b
queue.* == queue.a,queue.b
Java案例(配置)
java
@Bean // 定义交换机 - 建造者模式
public TopicExchange topicExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.topicExchange("exchange.topic").build();
}
@Bean // 定义队列 A
public Queue queueA() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("queue.topic.a").build();
}
@Bean // 定义队列 B
public Queue queueB() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("queue.topic.b").build();
}
// 绑定队列A和交换机并绑定模糊匹配的键(*.orange.*)
@Bean
public Binding bindingA(TopicExchange topicExchange, Queue queueA) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueA).to(topicExchange).with("*.orange.*");
}
// 绑定队列B和交换机并绑定模糊匹配的键(*.*.rabbit)
@Bean
public Binding bindingB1(TopicExchange topicExchange, Queue queueB) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueB).to(topicExchange).with("*.*.rabbit");
}
// 绑定队列B和交换机并绑定模糊匹配的键(lazy.#)
@Bean
public Binding bindingB2(TopicExchange topicExchange, Queue queueB) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueB).to(topicExchange).with("lazy.#");
}Java案例(测试)
java
@GetMapping("/message") // 发送消息
public void sendMessage(String msg) {
Message message = MessageBuilder.withBody(msg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)).build();
// 交换机的名字 - 键 - 消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange.topic", "hello.world.rabbit", message);
log.info("发送消息成功:{}", msg);
}
// 监听A队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue.topic.a")
public void receiveMessageA(Message msg) {
log.info("A接收到消息:{}", new String(msg.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
// 监听B队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue.topic.b")
public void receiveMessageB(String msg) {
log.info("B接收到消息:{}", msg);
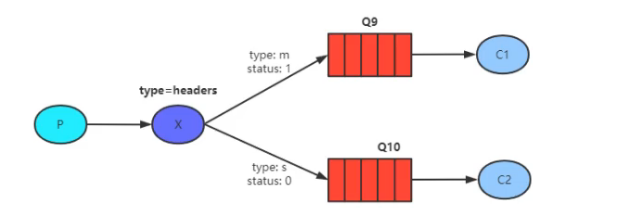
}头部交换机 - 使用较少
头部交换机跟以上三个交换机不同,它不采用路由键进行匹配。在消息中不仅仅有消息体还有消息头,头部交换机就是基于消息内容中的 Headers 进行匹配
Java案例(配置)
java
@Bean // 定义交换机 - 建造者模式
public HeadersExchange headersExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.headersExchange("exchange.headers").build();
}
@Bean // 定义队列 A
public Queue queueA() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("queue.headers.a").build();
}
@Bean // 定义队列 B
public Queue queueB() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("queue.headers.b").build();
}
// 绑定队列A和交换机
@Bean
public Binding bindingA(HeadersExchange headersExchange, Queue queueA) {
Map<String, Object> headerValues = new HashMap<>(); // 定义 headers 匹配用
headerValues.put("header1", "value-a1");
headerValues.put("header2", "value-a2");
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueA).to(headersExchange).whereAll(headerValues).match();
}
// 绑定队列B和交换机
@Bean
public Binding bindingB(HeadersExchange headersExchange, Queue queueB) {
Map<String, Object> headerValues = new HashMap<>();
headerValues.put("header1", "value-b1");
headerValues.put("header2", "value-b2");
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueB).to(headersExchange).whereAny(headerValues).match();
}Java案例(测试)
java
@GetMapping("/message") // 发送消息
public void sendMessage(String msg) {
// 消息属性
MessageProperties messageProperties = new MessageProperties();
messageProperties.setHeaders(Map.of(
"header1", "value-a1",
"header2", "value-a2"
));
// 消息
Message message = MessageBuilder
.withBody(msg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
.andProperties(messageProperties) // 消息属性
.build();
// 交换机的名字 - 键 - 消息
// 对于头部交换机来说,路由键无所谓,因为他是根据头来判断发送到那个队列的
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange.headers", "", message);
log.info("发送消息成功:{}", msg);
}
// 监听A队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue.headers.a")
public void receiveMessageA(Message msg) {
log.info("A接收到消息:{}", new String(msg.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
// 监听B队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue.headers.b")
public void receiveMessageB(String msg) {
log.info("B接收到消息:{}", msg);
}